Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Aspirin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<ref>[http://www.e-mjm.org/2018/v73n6/refractory-kawasaki-disease.pdf A case report of refractory kawasaki disease]</ref> | <ref>[http://www.e-mjm.org/2018/v73n6/refractory-kawasaki-disease.pdf A case report of refractory kawasaki disease]</ref> | ||
==Hutchinson | ==Hutchinson Gilford Progeria== | ||
Low dosis Aspirin 2-3 mg/Kg body weight is recommended for prevention of cardiovascular and stroke complications | Low dosis Aspirin 2-3 mg/Kg body weight is recommended for prevention of cardiovascular and stroke complications | ||
<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301300 Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome]</ref> | <ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301300 Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome]</ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:52, 24 January 2019
Aspirin is an NSAID [1] A recommendation of AAs-clopidogrel to maintain the patency of the stent following coronary intervention. Clopidogrel is a P2Y12 inhibiting platelet agent; the combination AAs Ticagrelor wasn´t better than clopidogrel+aspirin [2]
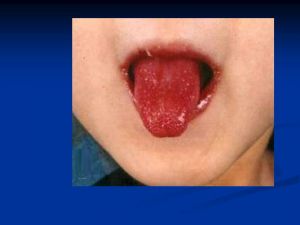
Kawasaki
Protocols recommend AAs and intravenous immunoglubin; however many cases have be shown to be refractory to this treatment [3]
Hutchinson Gilford Progeria
Low dosis Aspirin 2-3 mg/Kg body weight is recommended for prevention of cardiovascular and stroke complications [4]
ATC
Salicylic acid and derivates
- Acetylsalicylic acid (INN)