Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Rufinamide: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→ATC) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<ref>[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/epi.12689/epdf Safety and retention rate of rufinamide in 300 patients: a single pediatric epilepsy center experience]</ref> | <ref>[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/epi.12689/epdf Safety and retention rate of rufinamide in 300 patients: a single pediatric epilepsy center experience]</ref> | ||
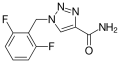
<gallery>File:Rufinamid.svg.png</gallery> | <gallery>File:Rufinamid.svg.png</gallery> | ||
It is an inductor of VYP 450 | |||
==Weblinks== | ==Weblinks== | ||
Revision as of 00:31, 26 August 2017
Lennox-Gastaut is a low prevalence epileptic syndrome (1:10000), and Cochrane Epilepsy Group concluded that treatment remain unconclusive. Otsuka et al. (2014) state rufinamide as an efficacious and well tolerated AED [1](cf. Alssad et Coren 2014) [2]
"Rufinamide received the status of orphan drug for epilepsy in 2004 in Europe"
[3]
It is an inductor of VYP 450
Weblinks
ATC
https://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=N03AF03
- ↑ Rufinamide as an adjunctive therapy for Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial in Japan
- ↑ Exposure to rufinamide and risks of CNS adverse events in drug-resistant epilepsy: a meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials
- ↑ Safety and retention rate of rufinamide in 300 patients: a single pediatric epilepsy center experience