Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Diacomit: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
m (todo) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
In December 2001 the European Medicines Agency (EMA) granted stiripentol orphan drug status (designation number EU/3/01/071) for the treatment of severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy (Dravet's syndrome). On 4 January 2007, the EMA granted the drug a marketing authorisation that is valid throughout the European Union | In December 2001 the European Medicines Agency (EMA) granted stiripentol orphan drug status (designation number EU/3/01/071) for the treatment of severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy (Dravet's syndrome). On 4 January 2007, the EMA granted the drug a marketing authorisation that is valid throughout the European Union | ||
[[Dravet's syndrome]] does not exist data for combined therapy both valproic acid or clobazam<ref>Aras et al 2015</ref> | [[Dravet's syndrome]] does not exist data for combined therapy both valproic acid or [[clobazam]]<ref>Aras et al 2015</ref> | ||
==ATC== | ==ATC== | ||
Revision as of 04:25, 1 April 2016
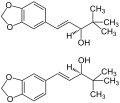
Diacomit contains 250 mg stiripentol[1][2]
In December 2001 the European Medicines Agency (EMA) granted stiripentol orphan drug status (designation number EU/3/01/071) for the treatment of severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy (Dravet's syndrome). On 4 January 2007, the EMA granted the drug a marketing authorisation that is valid throughout the European Union
Dravet's syndrome does not exist data for combined therapy both valproic acid or clobazam[4]
ATC
http://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=N03AX17
- ↑ http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/es_ES/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000664/WC500036518.pdf
- ↑ A new type of anticonvulsant, stiripentol. Pharmacological profile and neurochemical study. Arzneimittelforschung. 1984; 34(2):199-204.
- ↑ Stiripentol, a Putative Antiepileptic Drug, Enhances the Duration of Opening of GABAA-Receptor Channels
- ↑ Aras et al 2015