Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: Difference between revisions
m (→Links: todo) |
m (type) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
==[[Rufinamide]]== | ==[[Rufinamide]]== | ||
[http://www.ejpn-journal.com/article/S1090-3798(16)00004-0/abstract Safety and pharmacokinetic profile of rufinamide in pediatric patients aged less than 4 years with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: An interim analysis from a multicenter, randomized, active-controlled, open-label study] | [http://www.ejpn-journal.com/article/S1090-3798(16)00004-0/abstract Safety and pharmacokinetic profile of rufinamide in pediatric patients aged less than 4 years with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: An interim analysis from a multicenter, randomized, active-controlled, open-label study] | ||
==Clobazam== | ==Clobazam== | ||
[[File:Fneur-05-00225-g001.jpg|thumb|Archer et al. Ictal EEG features and peri-ictal SPECT of tonic seizures in LGS. Frontiers in Neurology 5 2014]] | [[File:Fneur-05-00225-g001.jpg|thumb|Archer et al. Ictal EEG features and peri-ictal SPECT of tonic seizures in LGS. Frontiers in Neurology 5 2014]] | ||
[[Clobazam]] was approved by FDA on 2011 as adjuntive treatment of | [[Clobazam]] was approved by FDA on 2011 as adjuntive treatment of seizures associated with LGS in patients 2 year and older | ||
<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4467745/pdf/tcrm-11-905.pdf Comprehensive overview: efficacy, tolerability, and cost-effectiveness of clobazam in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome]</ref> | <ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4467745/pdf/tcrm-11-905.pdf Comprehensive overview: efficacy, tolerability, and cost-effectiveness of clobazam in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome]</ref> | ||
Revision as of 04:29, 1 April 2016
Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (LGS[1]) is a difficult-to-treat form of childhood-onset epilepsy that most often appears between the second and sixth year of life. LGS is characterized by a triad of signs including frequent seizures of multiple types, an abnormal EEG pattern of less than 2.5 Hz slow spike wave activity,[2]
LGS children with a history of perinatal hypoxia or other perinatal event have earlier age of onset of seizures[3]
Links
LGS may evolve from West syndrome
Endoscopic epilepsy surgery: Emergence of a new procedure
Surgical options for patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrom epilepsia suppl. 55:21 4:21-8. doi: 10.1111/epi.12742.
Rufinamide
Clobazam
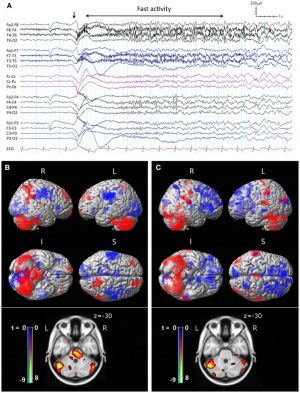
Clobazam was approved by FDA on 2011 as adjuntive treatment of seizures associated with LGS in patients 2 year and older [4]
stable dosage of clobazam for LGS are associated Epilepsia 55: 558(2014)