Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome: Difference between revisions
(spect todo) |
(concept and image credits) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
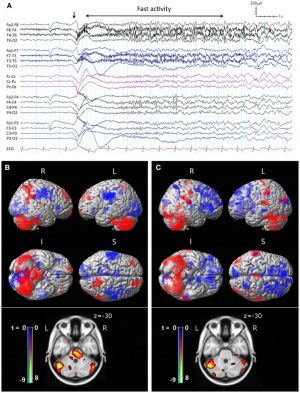
'''Lennox–Gastaut syndrome''' (LGS<ref>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4214194/</ref>) is a difficult-to-treat form of childhood-onset [[epilepsy]] that most often appears between the second and sixth year of life. LGS is characterized by a triad of signs including frequent seizures of multiple types, an abnormal EEG pattern of less than 2.5 Hz slow spike wave activity,<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Lennox%E2%80%93Gastaut_syndrome&oldid=699385431 wikipedia]</ref> | '''Lennox–Gastaut syndrome''' (LGS<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4214194/ Conceptualizing Lennox–Gastaut Syndrome as a Secondary Network Epilepsy]</ref>) is a difficult-to-treat form of childhood-onset [[epilepsy]] that most often appears between the second and sixth year of life. LGS is characterized by a triad of signs including frequent seizures of multiple types, an abnormal EEG pattern of less than 2.5 Hz slow spike wave activity,<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Lennox%E2%80%93Gastaut_syndrome&oldid=699385431 wikipedia]</ref> | ||
LGS children with a history of perinatal hypoxia or other perinatal event have earlier age of onset of seizures<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4489077/ Relationship of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome with perinatal event: A cross-sectional study]</ref> | LGS children with a history of perinatal hypoxia or other perinatal event have earlier age of onset of seizures<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4489077/ Relationship of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome with perinatal event: A cross-sectional study]</ref> | ||
Revision as of 22:21, 31 January 2016
Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (LGS[1]) is a difficult-to-treat form of childhood-onset epilepsy that most often appears between the second and sixth year of life. LGS is characterized by a triad of signs including frequent seizures of multiple types, an abnormal EEG pattern of less than 2.5 Hz slow spike wave activity,[2]
LGS children with a history of perinatal hypoxia or other perinatal event have earlier age of onset of seizures[3]
Links
Endoscopic epilepsy surgery: Emergence of a new procedure
Rufinamide
Clobazam
Clobazam was approved by FDA on 2011 as adjuntive treatment of seisures associated with LGS in patients 2 year and older [4]
stable dosage of clobazam for LGS are associated Epilepsia 55: 558(2014)