Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Aspirin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
m (→Links) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Aspirin is an | Aspirin is an [[Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug| NSAID]] | ||
<ref>https://karmel.miraheze.org/wiki/PenaRC2/profilaxis_AAS</ref> | <ref>https://karmel.miraheze.org/wiki/PenaRC2/profilaxis_AAS</ref> | ||
A recommendation of AAs-clopidogrel to maintain the patency of the stent following coronary intervention. Clopidogrel is a P2Y12 | A recommendation of AAs-[[clopidogrel]] to maintain the patency of the stent following coronary intervention. Clopidogrel is a P2Y12 inhibiting platelet agent; the combination AAs Ticagrelor wasn´t better than clopidogrel+aspirin | ||
<ref>https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/8/1/104/htm Clopidogrel versus Ticagrelor for Secondary Prevention after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting]>/ref> | <ref>[https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/8/1/104/htm Clopidogrel versus Ticagrelor for Secondary Prevention after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting]</ref> | ||
[[File:Kawasaki_tongue_1.jpg|thumb]] | |||
==[[Kawasaki disease|Kawasaki]]== | |||
Protocols recommend AAs and intravenous immunoglubin; however many cases have be shown to be refractory to this treatment | |||
<ref>[http://www.e-mjm.org/2018/v73n6/refractory-kawasaki-disease.pdf A case report of refractory kawasaki disease]</ref> | |||
==[[Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria]]== | |||
[[File:Progeri n1.jpg|thumb]] | |||
Low dosis Aspirin 2-3 mg/Kg body weight is recommended for prevention of cardiovascular and stroke complications | |||
<ref>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301300 Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome]</ref> | |||
==[[ATC]]== | |||
[[File:Under construction icon.png|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Aspirin-B-3D-balls.png|thumb]] | |||
Salicylic acid and derivates | |||
*Acetylsalicylic acid (INN) | |||
[https://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=N02BA01 N02BA01] | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
[https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-019-3872-0 Level and variation on quality of care in China: a cross-sectional study for the acute myocardial infarction patients in tertiary hospitals in Beijing] | [https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-019-3872-0 Level and variation on quality of care in China: a cross-sectional study for the acute myocardial infarction patients in tertiary hospitals in Beijing] | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[nl:aspirine]] | |||
{{Wikidata|Q18216}} | |||
[[Category:World Health Organization essential medicines]] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:36, 26 January 2019
Aspirin is an NSAID [1] A recommendation of AAs-clopidogrel to maintain the patency of the stent following coronary intervention. Clopidogrel is a P2Y12 inhibiting platelet agent; the combination AAs Ticagrelor wasn´t better than clopidogrel+aspirin [2]
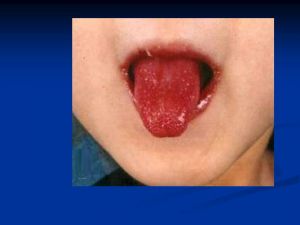
Kawasaki
Protocols recommend AAs and intravenous immunoglubin; however many cases have be shown to be refractory to this treatment [3]
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria
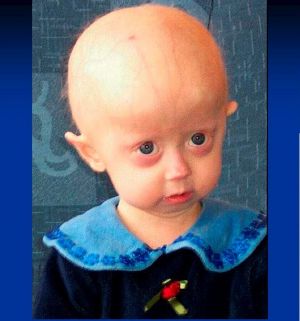
Low dosis Aspirin 2-3 mg/Kg body weight is recommended for prevention of cardiovascular and stroke complications [4]
ATC

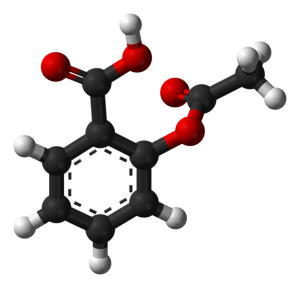
Salicylic acid and derivates
- Acetylsalicylic acid (INN)