Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (File:Nihms-803560-f0004.jpg) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
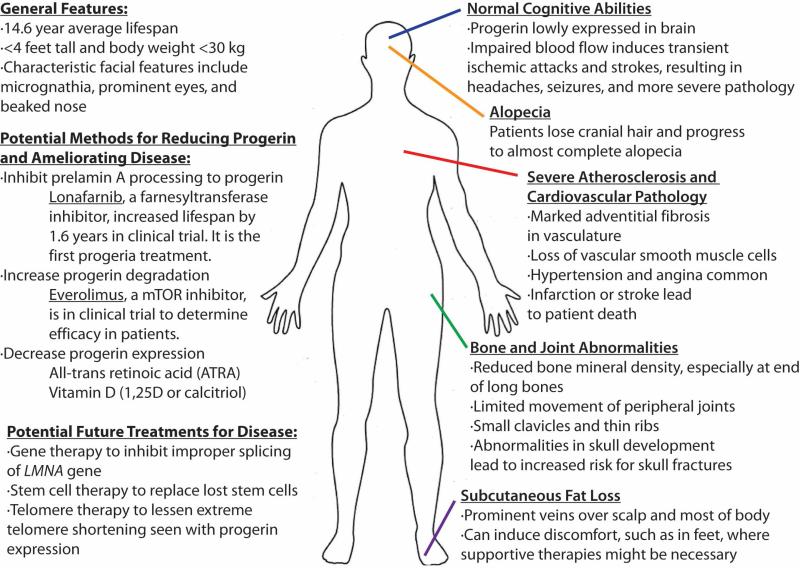
Hutchinson-Gilford Disease (or syndrome) Progeria | Hutchinson-Gilford Disease (or syndrome) Progeria ― early senescence in children with large skull, bird-like features, atrophy of skin, los subcutaneous fat, high serum lipid levels and early atherosclerotic changes in the vessels | ||
Progeria was first described in 1886 by two English surgeons Jonathan Hutchinson (Sir) and [[Hastings Gilford|H. Gilford]] <ref>Dictionary of Medical eponyms Firkin BG and JA Whitworth Roche </ref> | Progeria was first described in 1886 by two English surgeons Jonathan Hutchinson (Sir) and [[Hastings Gilford|H. Gilford]] <ref>Dictionary of Medical eponyms Firkin BG and JA Whitworth Roche </ref> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:30, 24 January 2019
Hutchinson-Gilford Disease (or syndrome) Progeria ― early senescence in children with large skull, bird-like features, atrophy of skin, los subcutaneous fat, high serum lipid levels and early atherosclerotic changes in the vessels Progeria was first described in 1886 by two English surgeons Jonathan Hutchinson (Sir) and H. Gilford [1]
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome: A premature aging disease caused by LMNA gene mutations
- ↑ Dictionary of Medical eponyms Firkin BG and JA Whitworth Roche