Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Zollinger-Ellinson syndrome: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(nl+ wp-lead) |
(→Links) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Zollinger–Ellison Syndrome (ZES) is caused by a non–beta islet cell (islet of Langerhans), gastrin-secreting tumor of the pancreas that stimulates the acid-secreting cells of the stomach (parietal cells) to maximal activity, with consequent gastrointestinal mucosal ulceration. ZES may occur sporadically or as part of an autosomal dominant familial syndrome called multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1). The primary tumor is usually located in the pancreas, duodenum or abdominal lymph nodes, but ectopic locations have also been described (e.g., heart, ovary, gallbladder, liver, kidney) | [[File:ZES endosc.jpg|thumb]] | ||
Zollinger–Ellison Syndrome (ZES) is caused by a non–beta islet cell ([[islet of Langerhans]]), gastrin-secreting tumor of the pancreas that stimulates the acid-secreting cells of the stomach (parietal cells) to maximal activity, with consequent gastrointestinal mucosal ulceration. ZES may occur sporadically or as part of an autosomal dominant familial syndrome called multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1). The primary tumor is usually located in the pancreas, duodenum or abdominal lymph nodes, but ectopic locations have also been described (e.g., heart, ovary, gallbladder, liver, kidney). | |||
[[nl: | ==Links== | ||
*Sara Massironi et al. 2015 Somatostatin analogs for gastric carcinoids: for many, but not all [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462718/ World J Gastroenterol. ; 21(22): 6785–6793] | |||
*Sunil Dasha et al. 2015 [http://gastro.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=25698559 Gastroenterol. Rep. 1-8] | |||
{{Wikidata|Q218712}} | |||
[[nl:Zollinger-Ellison-syndroom]] | |||
<references/> | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:04, 30 November 2015
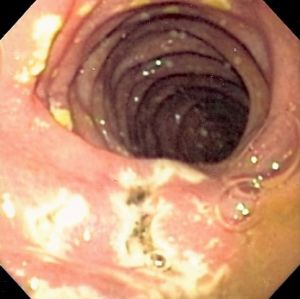
Zollinger–Ellison Syndrome (ZES) is caused by a non–beta islet cell (islet of Langerhans), gastrin-secreting tumor of the pancreas that stimulates the acid-secreting cells of the stomach (parietal cells) to maximal activity, with consequent gastrointestinal mucosal ulceration. ZES may occur sporadically or as part of an autosomal dominant familial syndrome called multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1). The primary tumor is usually located in the pancreas, duodenum or abdominal lymph nodes, but ectopic locations have also been described (e.g., heart, ovary, gallbladder, liver, kidney).
Links
- Sara Massironi et al. 2015 Somatostatin analogs for gastric carcinoids: for many, but not all World J Gastroenterol. ; 21(22): 6785–6793
- Sunil Dasha et al. 2015 Gastroenterol. Rep. 1-8