Wikisage, the free encyclopedia of the second generation, is digital heritage
Valproate: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
erithema nodosum was observed associated with valproate therapy | erithema nodosum was observed associated with valproate therapy | ||
<ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4695434/pdf/ad-27-765.pdf Erythema Nodosum Associated with Valproate ]</ref> | <ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4695434/pdf/ad-27-765.pdf Erythema Nodosum Associated with Valproate ]</ref> | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
{{Wikidata|Q240642}} | {{Wikidata|Q240642}} | ||
==ATC== | |||
http://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=N03AX11 | |||
{| style="background:Ivory; color:black" border=1 cellspacing=1 cellpadding=5 | {| style="background:Ivory; color:black" border=1 cellspacing=1 cellpadding=5 | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
https://www.drugs.com/pro/divalproex-extended-release.html | https://www.drugs.com/pro/divalproex-extended-release.html | ||
{{refs}} | |||
[[Category:Epilepsy]] | [[Category:Epilepsy]] | ||
[[Category:Anticonvulsants]] | [[Category:Anticonvulsants]] | ||
Revision as of 22:41, 18 May 2019
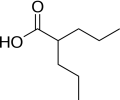
Valproic acid is a carboxylic acid, a well probed AED[1], with a high teratogenic potential.[2] [3] [4],
may alter bone metabolism
[5] erithema nodosum was observed associated with valproate therapy [6]
Links
Fanconi syndrome
Progressive myoclonic epilepsy with Fanconi syndrome
Autism
Hipothyroidism
Hypothyroidism may exacerbate valproate-related hyperammonemic delirium
Vitamin B2
ATC
http://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=N03AX11
extended release
https://www.drugs.com/pro/divalproex-extended-release.html